Continuous deployment of a Phoenix project using GitLab CI/CD
In this article, we will walk through the setup of GitLab CI/CD pipelines to run the tests and deploy the latest version for each merge on master. We assume that you already have a Phoenix project up and running, and created a GitLab repository for your project.
We need to create the gitlab-ci.yml file at the root of the repository. In this file, we will define the different jobs that are required to deploy a new version to production automatically:
- init: we download the dependencies and build the project;
- lint: we make sure that the code follows our style guide;
- test: we make nothing has broken with our changes;
- deploy: push the new version to production. This step is only executed when we merge a feature branch on master.
TLDR; jump at the end of the article to have the full gitlab-ci.yml config file.
Default settings
I the gitlab-ci.yml file we define:
- the list of stages;
- the env variables that are used by Phoenix for the database;
- the default settings for Elixir and JavaScript we will re-use for each jobs.
stages:
- init
- lint
- test
- deploy
variables:
POSTGRES_DB: test_test
POSTGRES_HOST: postgres
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: 'postgres'
MIX_ENV: 'test'
.elixir_default: &elixir_default
image: elixir:1.8
before_script:
- mix local.hex --force
- mix local.rebar --force
.javascript_default: &javascript_default
image: node:alpine
before_script:
- cd assetsInit stage
In the init stage, we set up the environment for the next jobs by compiling the project, downloading the dependencies and saving the artifacts.
elixir_compile:
<<: *elixir_default
stage: init
script:
- apt-get update
- apt-get install -y postgresql-client
- mix deps.get --only test
- mix compile --warnings-as-errors
artifacts:
paths:
- mix.lock
- _build
- deps
javascript_deps:
<<: *javascript_default
stage: init
script:
- npm install --progress=false
artifacts:
paths:
- assets/node_modulesLint stage
Credo for Elixir
We use Credo to lint the Elixir part of the project. To install it we add its dependency to mix.exs.
defp deps do
[
{:credo, "~> 1.0.0", only: [:dev, :test], runtime: false}
]
endThere are plenty of settings that are available with Credo to match your style guide.
Eslint and Prettier for JavaScript
For JavaScript, we use Eslint + Prettier. We add the required dependencies that are automatically added in assets/package.json.
cd assets && npm install --save-dev babel-eslint eslint eslint-config-prettier eslint-plugin-prettier prettierWe define the Eslint config in assets/.eslintrc.
{
"parser": "babel-eslint",
"extends": ["eslint:recommended", "prettier"],
"plugins": ["prettier"],
"rules": {
"prettier/prettier": "error"
},
"env": {
"browser": true,
"jest": true,
"node": true
}
}And the Prettier config in assets/.prettierrc.
{
"trailingComma": "es5",
"tabWidth": 2,
"semi": false,
"singleQuote": false
}Finally, we update assets/package.json to add the lint task.
"scripts": {
"deploy": "webpack --mode production",
"watch": "webpack --mode development --watch",
"lint": "eslint . --max-warnings=0"
}CI jobs
We can now add the jobs in gitlab-ci.yml to run the linters in the CI.
elixir_lint:
<<: *elixir_default
stage: lint
script:
- mix format --check-formatted
- mix credo --strict
javascript_lint:
<<: *javascript_default
stage: lint
script:
- npm run lintTest
Jest for JavaScript
We will use the test task in our assets/package.json to execute the client tests. I recommend using Jest. It’s a fast test framework, has an easy way to mock dependencies, has a nice interactive CLI, and it comes with jsdom by default.
cd assets && npm install --save-dev jestYou can setup Jest config by running npx jest --init.
We run Jest in the test task by adding it to the assets/package.json
"scripts": {
...
"test": "jest"
},CI jobs
Let’s add the test jobs in our gitlab-ci.yml file
elixir_test:
<<: *elixir_default
stage: test
services:
- postgres:11.3
script:
- mix ecto.create
- mix ecto.migrate
- mix test
javascript_test:
<<: *javascript_default
stage: test
script:
- npm run testDeploy
We will use Gigalixir as a hosting platform. It’s a PaaS designed for Elixir and Phoenix. The deployment is similar to Heroku, where we deploy by pushing to a remote branch. Moreover, it has a free plan that allows us to run our app with a Postgres database.
Before adding the deployment config for GitLab, we need to make sure everything is set up for Gigalixir locally.
First we need to install the Gigalixir command line tools:
pip install gigalixir --ignore-installed sixAnd then login:
gigalixir loginWe can now create a new app with a Postgres database on their platform:
gigalixir create -n my-app
gigalixir pg:create --freeGigalixir has a good documentation to config the production environment of our Phoenix project.
We need to delete prod.secret.exs file since Gigalixir is handling it for us and we will use the environment variable instead. Then we open prod.exs and delete the import of import_config "prod.secret.exs". And finally, we add the configuration to connect to Gigalixir.
config :my_app, MyAppWeb.Endpoint,
http: [port: {:system, "PORT"}],
url: [host: System.get_env("APP_NAME") <> ".gigalixirapp.com", port: 80],
secret_key_base: Map.fetch!(System.get_env(), "SECRET_KEY_BASE"),
server: true
config :my_app, MyApp.Repo,
adapter: Ecto.Adapters.Postgres,
url: System.get_env("DATABASE_URL"),
ssl: true,
pool_size: 2The environment variables are automatically set by Gigalixir when we deploy.
Specify versions
Next, we need to specify the versions we are using to build the project. At the root of the repository, we create the files:
elixir_buildpack.config
elixir_version=1.8.2
erlang_version=21.2.5phoenix_static_buildpack.config
node_version=10.16.0Build client side
We need to add a new file at the root of the repository called compile and paste the following lines:
npm run deploy
cd $phoenix_dir
mix "${phoenix_ex}.digest"We are now ready to deploy. Commit the changes and manually push the first version to Gigalixir to make sure everything works as expected.
git push gigalixir masterWe can navigate to the link of the app to check or check the logs by running
gigalixir logs.
CI job
We are now ready to add the deploy step in our gitlab-ci.yml file.
deploy:
stage: deploy
script:
- git remote add gigalixir $GIGALIXIR_REMOTE_URL
- git push -f gigalixir HEAD:refs/heads/master
when: manual
only:
- masterNote that you can remove the line when: manual if you want to deploy a new version to production every time you merge to master. Otherwise, with when: manual you will need to go on GitLab pipeline interface and start this step manually.
We added a new environment variable $GIGALIXIR_REMOTE_URL. You need to set its value in GitLab project’s settings (settings → CI/CD → variables). It should have the following format:
https://name%40mail-provider.com:password@git.gigalixir.com/my-project-name.gitYou can find the values by opening ~/.netrc
machine git.gigalixir.com
login doe@fastmail.com
password 1234-5678-9So, for our my-app project the remove URL is:
https://doe%40fastmail.com:1234-5678-9@git.gigalixir.com/my-app.gitLet’s merge our changes on master and watch GitLab deploying our app on Gigalixir 🎉
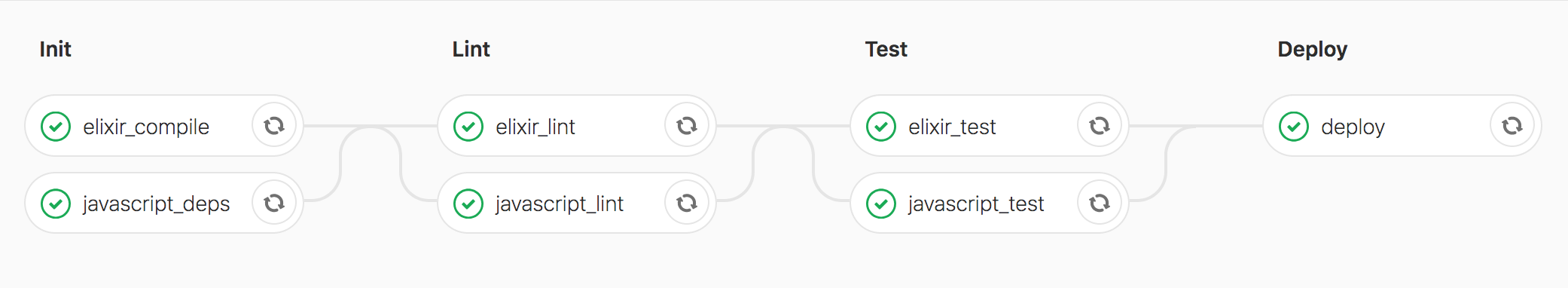
The all together gitlab-ci.yml
variables:
POSTGRES_DB: test_test
POSTGRES_HOST: postgres
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: 'postgres'
MIX_ENV: 'test'
stages:
- init
- lint
- test
- deploy
.elixir_default: &elixir_default
image: elixir:1.8
before_script:
- mix local.hex --force
- mix local.rebar --force
.javascript_default: &javascript_default
image: node:alpine
before_script:
- cd assets
elixir_compile:
<<: *elixir_default
stage: init
script:
- apt-get update
- apt-get install -y postgresql-client
- mix deps.get --only test
- mix compile --warnings-as-errors
artifacts:
paths:
- mix.lock
- _build
- deps
elixir_lint:
<<: *elixir_default
stage: lint
script:
- mix format --check-formatted
- mix credo --strict
elixir_test:
<<: *elixir_default
stage: test
services:
- postgres:11.3
script:
- mix ecto.create
- mix ecto.migrate
- mix test
javascript_deps:
<<: *javascript_default
stage: init
script:
- npm install --progress=false
artifacts:
paths:
- assets/node_modules
javascript_lint:
<<: *javascript_default
stage: lint
script:
- npm run lint
javascript_test:
<<: *javascript_default
stage: test
script:
- npm run test
deploy:
stage: deploy
script:
- git remote add gigalixir $GIGALIXIR_REMOTE_URL
- git push -f gigalixir HEAD:refs/heads/master
when: manual
only:
- master